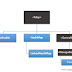
Map is used when you need keyed elements. It means, Map stores your data with a key. This map concept is totally different from other collections like List, Set and Queue. There are four main implementations.
- HashMap
- LinkedHashMap
- HashTable
- TreeMap
Traverse on a Map
- Using Iterator
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, 10);
map.put(8, 50);
map.put(5, 10);
map.put(10, 90);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer key = iterator.next();
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.print(key + "-");
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
}
}
- Using enhanced for loop
for(Integer key : map.keySet()){
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.print(key + "-");
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
Basic operations on Map interface
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, 10);
map.put(8, 50);
map.put(5, 10);
map.put(10, 90);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); //check map is empty or not4
System.out.println(map.size()); //get the size of the map
System.out.println(map.keySet()); //get the keys
System.out.println(map.values()); //get the values
System.out.println(map.put(5, 100)); //replace value on given key
System.out.println(map);
map.clear(); //clear map
System.out.println(map);
}
}
You may look at the following code to understand how to use maps to find distinct words.
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
String statement = "If it is true this is also true and that is also ";
String[] arr = statement.toLowerCase().split(" ");
for(String s : arr){
Integer i = map.get(s);
map.put(s, (i==null) ? 1 : i+1);
}
System.out.println(map.size() + " distinct words : " + map);
}
}import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class StringOccurence {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "easy java se";
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Map<Character, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for(char c : chars){
if(map.containsKey(c)){
map.put(c, map.get(c)+1);
}
else{
map.put(c, 1);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}HashMap vs LinkedHashMap vs HashTable vs TreeMap
Map interface
 Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
11:45 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
11:45 AM
Rating:
 Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
11:45 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
11:45 AM
Rating:






No comments: