Spring Boot is a widely used and very popular enterprise-level high-performance framework. Here are some best practices and some tips you can use to improve your Spring Boot application and make it more efficient. This article will be a little longer, and it will take some time to completely reading the article.
Proper packaging style
- Proper packaging will help to understand the code and the flow of the application easily.
- You can structure your application with meaningful packaging.
- You can include all your controllers in a separate package, services in a separate package, util classes in a separate package…etc. This style is very convenient for small-sized microservices.
- If you are working on a huge code base, a feature-based approach can be used. You can decide on your requirement.
Based on type
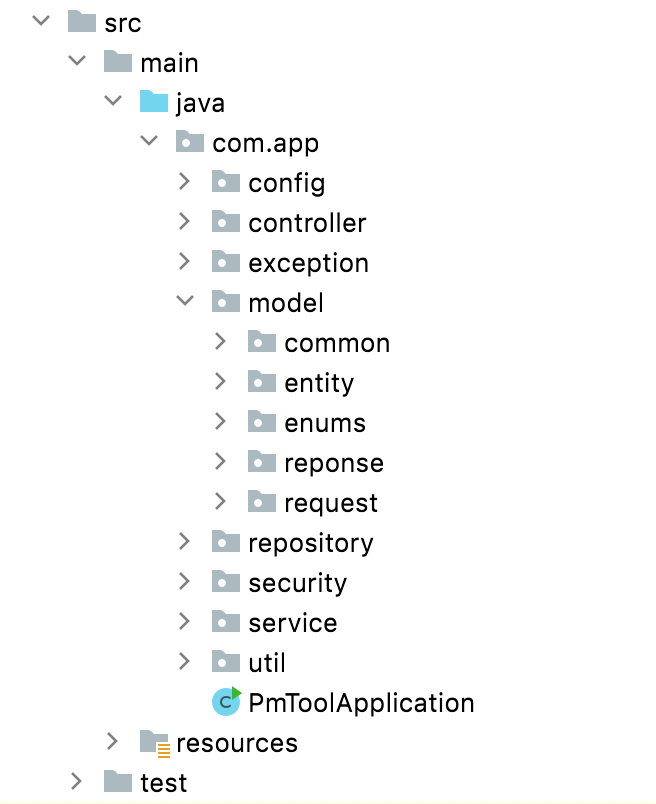
Based on feature
Use design patterns
- No complaints. Design patterns are already best practices.
- But you must identify the place where you can use them.
- Please check this article to understand “how to use the Builder design pattern” in our Spring Boot applications.
Use Spring Boot starters

- This is a cool feature of Spring Boot.
- We can very easily use starter dependencies without adding single dependencies one by one. These starter dependencies are already bundled with the required dependencies.
- For example, if we add spring-boot-starter-web dependency, by default it is bundled with jackson, spring-core, spring-mvc, and spring-boot-starter-tomcat dependencies.
- So we don’t need to care about adding dependencies separately.
- And also it helps us to avoid version mismatches.
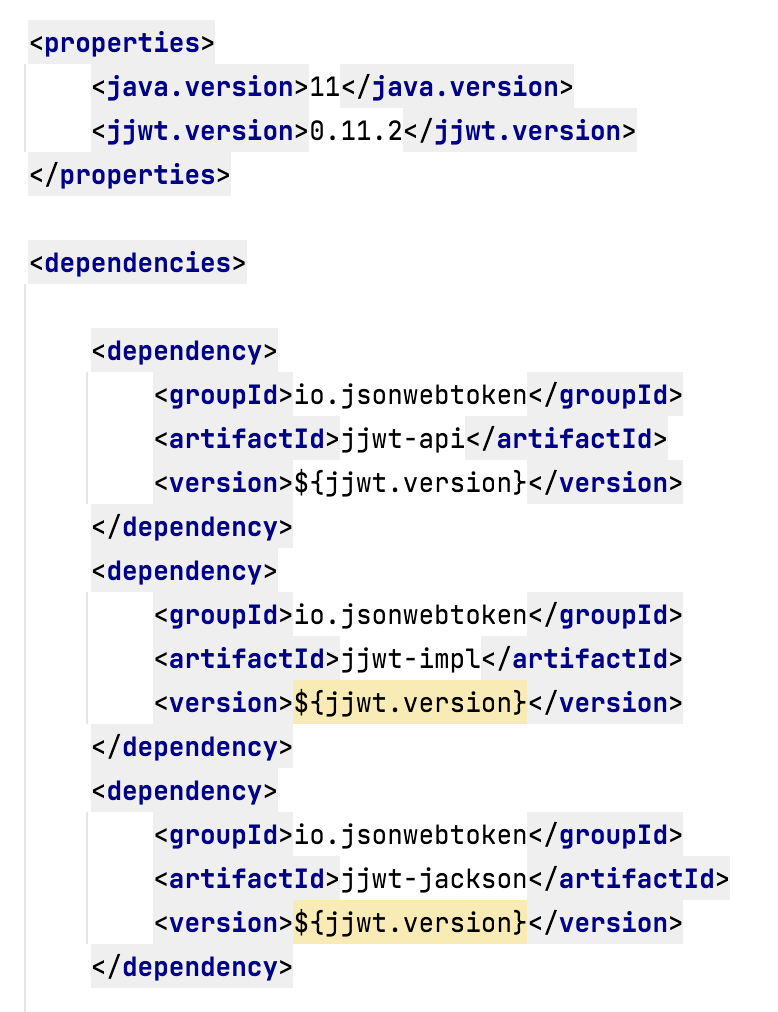
Use proper versions of the dependencies
- It is always recommended to use the latest stable GA versions.
- Sometimes it may vary with the Java version, server versions, the type of the application…etc.
- Do not use different versions for the same package and always use <properties> to specify the version if there are multiple dependencies.
Use Lombok
- As a Java developer, you have probably heard of the Lombok project.
- Lombok is a Java library that can be used to reduce your code and allow you to write clean code using its annotations.
- For example, you may use plenty of lines for getters and setters in some classes like entities, request/response objects, dtos, etc.
- But if you use Lombok, it is just one line; you can use @Data, @Getter or @Setter as per your requirement.
- You can use Lombok logger annotations as well. @Slf4j is recommended.
- Check this file for your reference.
Use constructor injection with Lombok

- When we talk about dependency injection, there are two types.
- One is “constructor injection” and the other is “setter injection”. Apart from that, you can also use “field injection” using the very popular @Autowired annotation.
- But we highly recommend using Constructor injection over other types. Because it allows the application to initialize all required dependencies at the initialization time.
- This is very useful for unit testing.
- The important thing is, that we can use the @RequiredArgsConstructor annotation by Lombok to use constructor injection.
- Check this sample controller for your reference.
Use slf4j logging

- Logging is very important.
- If a problem occurs while your application is in production, logging is the only way to find out the root cause.
- Therefore, you should think carefully before adding loggers, log message types, logger levels, and logger messages.
- Do not use System.out.print()
- Slf4j is recommended to use along with logback which is the default logging framework in Spring Boot.
- Always use slf4j { } and avoid using String interpolation in logger messages. Because string interpolation consumes more memory.
- Please check this file for your reference to get an idea about, implementing a logger.
- If you are in a microservices environment, you can use the ELK stack.
Use Controllers only for routing

- Controllers are dedicated to routing.
- It is stateless and a singleton.
- The DispatcherServlet will check the @RequestMapping on the Controllers
- Controllers are the ultimate target of requests, and then requests will be handed over to the service layer and processed by it.
- The business logic should not be in the controllers.
Use Services for business logic
- The complete business logic is outlined here, including validations, caching, and other relevant details.
- Services communicate with the persistence layer and receive the results.
- Services are also singletons.
Read the complete article: Spring Boot Best Practices for Developers
This is not the end. There are a lot of small tips and practices. Let’s look at them in the next articles. You can view the same article on my Medium profile.
Spring Boot Best Practices for Developers
 Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
4:35 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
4:35 PM
Rating:
 Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
4:35 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by Ravi Yasas
on
4:35 PM
Rating:





No comments: